Sponsored Link
lnav Features
Support for the following log file formats:
Syslog, Apache access log, strace, tcsh history, and generic log files with timestamps. The file format is automatically detected when the file is read in.
Histogram view:
Displays the number of log messages per bucket-of-time. Useful for getting an overview of what was happening over a long period of time.
Filters:
Display only lines that match or do not match a set of regular expressions. Useful for removing extraneous log lines that you are not interested in.
"Live" operation:
Searches are done as you type; new log lines are automatically loaded and searched as they are added; filters apply to lines as they are loaded; and, SQL queries are checked for correctness as you type.
Automatic tailing:
The log file view automatically scrolls down to follow new lines that are added to files. Simply scroll up to lock the view in place and then scroll down to the bottom to resume tailing.
Time-of-day ordering of lines:
The log lines from all the files are loaded and then sorted by time-of-day. Relieves you of having to manually line up log messages from different files.
Syntax highlighting:
Errors and warnings are colored in red and yellow, respectively. Highlights are also applied to: SQL keywords, XML tags, file and line numbers in Java backtraces, and quoted strings.
Navigation:
There are hotkeys for jumping to the next or previous error or warning and moving forward or backward by an amount of time.
Use SQL to query logs:
Each log file line is treated as a row in a database that can be queried using SQL. The columns that are available depend on logs file types being viewed.
Command and search history:
Your previously entered commands and searches are saved so you can access them between sessions.
Compressed files:
Compressed log files are automatically detected and uncompressed on the fly.
Install lnav on ubuntu 15.10
Open the terminal and run the following command
sudo apt-get install lnav
Using lnav
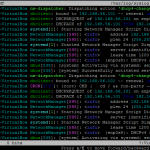
If you want to view logs using lnav you can do using the following command by default it shows syslogs
lnav
If you want to view specific logs provide the path
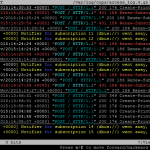
If you want to view CUPS logs run the following command from your terminal
lnav /var/log/cups